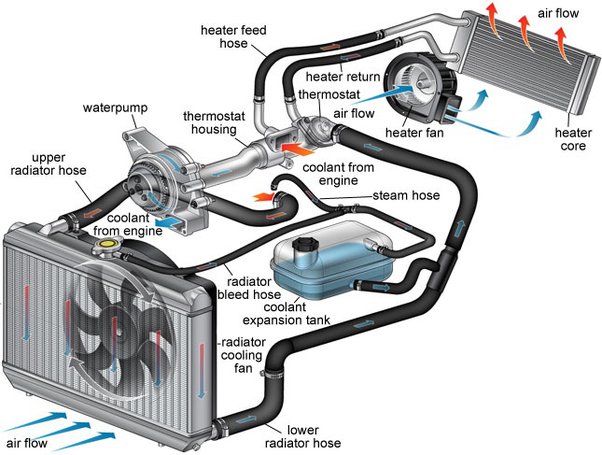
How Do You Know If You Have a Bad Oil Cooler?
You have a bad oil cooler if you notice oil in the coolant or coolant in the oil. An overheating engine can also indicate a failing oil cooler.
Understanding vehicle maintenance is crucial for ensuring your car runs smoothly and efficiently. One component that might not get much attention but is vital for engine health is the oil cooler. This small but essential device maintains optimal oil temperature and prevents engine overheating.
Signs of a bad oil cooler can be subtle, and ignoring them might lead to severe engine damage. Recognizing the symptoms early on is key to avoiding costly repairs. Engaging with this topic helps vehicle owners recognize the importance of their oil cooler and encourages proactive maintenance, reflecting a commitment to informative, reader-friendly content that supports effective vehicle care.
Symptoms Of A Malfunctioning Oil Cooler
Ensuring your engine runs smoothly involves many components, one of which is the oil cooler. This vital part regulates the oil temperature, preventing your engine from overheating. Know the warning signs of a struggling oil cooler to avoid costly repairs.
Oil In The Cooling System
Discovering oil in your cooling system is a red flag. It suggests your oil cooler is leaking internally, allowing oil and coolant to mix. Look for oily residue inside your radiator or coolant reservoir.
Coolant In The Oil Pan
Similarly, spotting coolant in your oil pan is a telltale symptom. Check your oil dipstick for a frothy, milky substance. This indicates that the leak is allowing coolant to seep into your engine oil.
Engine Overheating
If your engine abruptly overheats, the oil cooler might be to blame. Unregulated oil temperatures can lead to serious engine damage. Watch your temperature gauge and engine performance closely.

Credit: www.carparts.com
Analyzing Coolant Contamination
Oil coolers play a crucial role in maintaining your engine’s health. When they fail, coolant contamination is a telltale sign. Understanding how to spot a compromised oil cooler can save your engine from severe damage. Here’s how you can identify if your vehicle’s oil cooler is in trouble by analyzing your coolant for contamination.
Visual Inspection For Milky Residue
A clear indication of oil cooler issues appears when inspecting the coolant. Look for a milky, brownish residue on your dipstick or in the coolant reservoir. This is often a sign that oil is mixing with the coolant. Another area to inspect is the radiator cap. Open it with care and search for the same milky substance.
Using Chemical Test Kits
Detecting contamination early is key. Chemical test kits are reliable tools for this. These kits can confirm the presence of oil in the coolant with a simple color change. Here’s how to use one:
- Read the instructions on the chemical test kit carefully.
- Collect a sample of the coolant in a clean container.
- Add the specified chemicals to the sample.
- Observe the color change.
- Compare the result with the chart provided in the kit to confirm contamination.
Measuring Oil Temperature
Your engine’s health hinges on maintaining the right oil temperature. But how do you know if your oil cooler is failing? Tracking your oil’s heat levels offers revealing clues. Let’s dive into understanding and monitoring these temperatures effectively.
Normal Operating Ranges
Different cars have different norms. Typically, oil temperature should sit between 180°F and 200°F (82°C – 93°C). Straying far from this range signals trouble. High oil temperatures can indicate a cooler in distress. Prolonged excessive heat degrades oil, compromising engine protection. Low temperatures, while less common, suggest that oil may not be reaching optimal efficiency levels.
| Condition | Temperature |
|---|---|
| Normal Range | 180°F – 200°F |
| High Temp Concern | Above 230°F |
| Low Temp Concern | Below 160°F |
Tools For Monitoring Oil Temp
To keep tabs on oil temperatures, consider these tools:
- Digital gauges for real-time monitoring
- Analog dials for a classic look
- Smartphone apps that connect to sensors
- Onboard diagnostics (OBD II) scanners with temperature readings
Accurate tools ensure you respond promptly to prevent damage. Choose one that suits your needs and skill level.
Pressure Testing The Oil Cooler
Ensuring your vehicle’s oil cooler works properly is crucial. A bad oil cooler can lead to engine overheating and damage. Pressure testing helps to check the health of your oil cooler. This test can reveal leaks and weaknesses in the cooler’s structure. The next sections guide you through the testing process.
Procedure For Conducting A Pressure Test
Pressure testing the oil cooler is a clear-cut process:
- Gather the necessary tools: a pressure tester and adapters for your vehicle’s specific oil cooler.
- Locate the oil cooler and disconnect it from the engine.
- Attach the pressure tester to the oil cooler’s inlet.
- Apply pressure as specified in the vehicle’s manual.
- Maintain the pressure for a time suggested by the manufacturer.
Interpreting Test Results
Reading the results from a pressure test tells you about the cooler’s condition:
- If the pressure holds steady, the cooler is in good shape.
- Pressure drop indicates a leak or crack in the cooler.
For precise results, always refer to your vehicle’s specifications.
Important: If a leak is present, seek professional repairs or consider a replacement.
Pros And Cons Of Oil Cooler Replacement
Assessing the need for an oil cooler replacement can be a critical decision for any vehicle owner. An effective oil cooler contributes to the engine’s longevity by keeping the oil at an optimal temperature. Yet, understanding when to repair or replace can be perplexing. The following examination dives into the intricacies of oil cooler replacement through a cost-benefit analysis and evaluating repair versus replacement.
Cost-benefit Analysis
Embarking on an oil cooler replacement journey entails weighing the costs against the potential benefits.
Pros:- Enhanced Engine Performance: A new oil cooler maintains oil viscosity, ensuring smooth engine operation.
- Prevents Overheating: Keeping engine temperatures down to prevent damage.
- Long-Term Savings: Curtails the likelihood of severe engine damage, reducing future repair expenses.
- Immediate Cost: High upfront payment for the new oil cooler and labor.
- Varying Quality: Replacement parts may differ in quality, affecting performance.
- Downtime: Vehicle unavailability during the replacement process.
A table can succinctly display this financial evaluation:
| Aspect | Cost | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Part | Variable | Reliability |
| Labor | Depends on the hour | Professional Installation |
| Future Repairs | Reduced Probability | Cost Savings |
Considering Repair Vs Replacement
The choice between repairing or replacing an oil cooler must factor in several aspects.
Repair:- Economical: Often less costly than a full replacement.
- Faster Turnaround: Quicker than installing a new unit.
- Extended Usability: Can prolong the life of the current oil cooler.
- Lasting Solution: Can potentially offer a more permanent fix to cooling issues.
- Warranties: New coolers often come with manufacturer guarantees.
- Updated Technology: Access to the latest cooling technology advancements.
Clearly, the decision pivots on the current condition of the oil cooler, the vehicle’s age, and the preferred outcome. Initial costs may be higher for a replacement, but the long-term benefits could justify the expenditure for those seeking reliability and a potentially warranty-backed peace of mind.

Credit: www.carparts.com
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Keeping your oil cooler in top shape matters. It prevents engine overheating. It also assures smooth vehicle operations. Here are some preventive maintenance tips to follow.
Regularly Scheduled Oil Changes
Changing oil on time is crucial. It keeps the oil cooler functional. It prevents build-up inside the cooler. Stick to manufacturer’s recommendations for oil change intervals. Use the right oil type to keep your oil cooler clean. This will help spot issues early on.
Checking Cooler Lines And Fittings
Leaks in oil cooler lines can cause big problems. Inspect lines and fittings regularly. Look for signs of wear or damage. Tight connections are important. Replace any worn parts promptly. This will prevent leaks and ensure the oil cooler stays effective.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Oil Change | As per manufacturer’s guidelines |
| Inspection of Cooler Lines | Every oil change or immediately if leaks are noticed |
- Use quality engine oil
- Maintain clean oil cooler fins
- Promptly address leaks or damage

Credit: www.yourmechanic.com
Frequently Asked Questions For How Do You Know If You Have A Bad Oil Cooler?
What Are Signs Of A Failing Oil Cooler?
An oil cooler failure often manifests through oil in the coolant, overheating engine, or visible coolant leaks. These signs indicate the oil cooler may be compromised, necessitating a check or replacement.
Can A Bad Oil Cooler Cause Engine Damage?
Yes, a malfunctioning oil cooler can lead to engine damage. It can cause oil and coolant to mix or result in the engine overheating, both of which are harmful to engine components and may lead to costly repairs.
How To Test For A Defective Oil Cooler?
To test for a defective oil cooler, check for cross-contamination by inspecting the coolant for oil presence or the oil for coolant. A pressure test can also help determine if there’s a leak in the oil cooler.
What Is The Lifespan Of An Oil Cooler?
An oil cooler typically lasts for the life of the engine, but its lifespan can vary. Factors like maintenance, driving habits, and quality of the cooler can affect its longevity; some may need replacement after 100,000 miles.
Conclusion
Recognizing a faulty oil cooler is essential for vehicle health. Symptoms like oil in the coolant, overheating engines, or poor performance signal trouble. Prompt attention saves money and extends engine life. Check your vehicle regularly and consult a mechanic if these signs emerge.
Protect your engine; stay vigilant for oil cooler failures.