Can Low Oil Cause Coolant Leak
Low oil levels alone do not directly cause coolant leaks. A vehicle’s oil and coolant systems are typically separate.
A coolant leak often triggers concern among vehicle owners. It’s a common problem that can lead to overheating and engine damage if not addressed promptly. Coolant, also known as antifreeze, circulates through the engine to maintain optimal operating temperatures. While low engine oil does not cause coolant to leak, it can exacerbate engine overheating, which can then lead to increased pressure and potential leaks in the cooling system.
Maintaining proper fluid levels for both oil and coolant is essential for the health of your engine. Diagnosing and repairing coolant leaks early helps preserve the longevity and performance of your vehicle, ensuring you stay safe on the road.
The Mechanics Of Engine Lubrication
Understanding the mechanics of engine lubrication is crucial for any vehicle owner. Proper lubrication ensures smooth operation and a long life for an engine. Oil coats the engine’s moving parts, preventing excessive friction. It serves as a barrier between these parts, reducing wear and tear.
Roles Of Oil In Engine Health
Engine oil plays several pivotal roles:
- Lubrication: Minimizes friction between moving components.
- Cooling: Carries away heat from critical areas.
- Cleaning: Collects debris and sediments, keeping the engine clean.
- Protecting: Provides a seal between piston rings and cylinder walls.
- Preventing Corrosion: Oil shields internal parts from rust.
Impact Of Low Oil On Engine Components
Low oil levels can lead to catastrophic effects on an engine. Here’s a glance at potential risks:
| Component | Impact of Low Oil |
|---|---|
| Bearings | Dry out and potentially seize up without adequate lubrication. |
| Pistons | Excessive wear due to increased friction. |
| Crankshaft | Can overheat and warp, causing engine imbalance. |
| Valvetrain | Noise increases and components degrade faster. |
When the oil level drops, these components lose the protection they need. Temperatures rise and parts may start to warp. In some cases, this can lead to a breach in the engine block or head gasket. Suddenly, coolant can begin to leak. A leak often emerges as oil fails to perform its critical roles. Accurate and regular oil checks remain a top practice in preventing engine damage and subsequent coolant leaks.
Coolant System Fundamentals
The efficient operation of an engine relies heavily on its cooling system. The system regulates the engine’s temperature, preventing overheating. Understanding how it functions is key to diagnosing issues such as coolant leaks.
Purpose Of Coolant In An Engine
Coolant, also known as antifreeze, serves critical roles in an engine:
- Absorbs heat from the engine to prevent damage.
- Reduces the freezing point in cold climates.
- Raises the boiling point to allow higher operating temperatures.
- Prevents corrosion inside the engine’s cooling passages.
Components Of The Coolant System
The coolant system consists of various parts working together:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Radiator | Dispels heat away from the coolant. |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant throughout the system. |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant flow based on temperature. |
| Hoses | Transports coolant to and from the engine. |
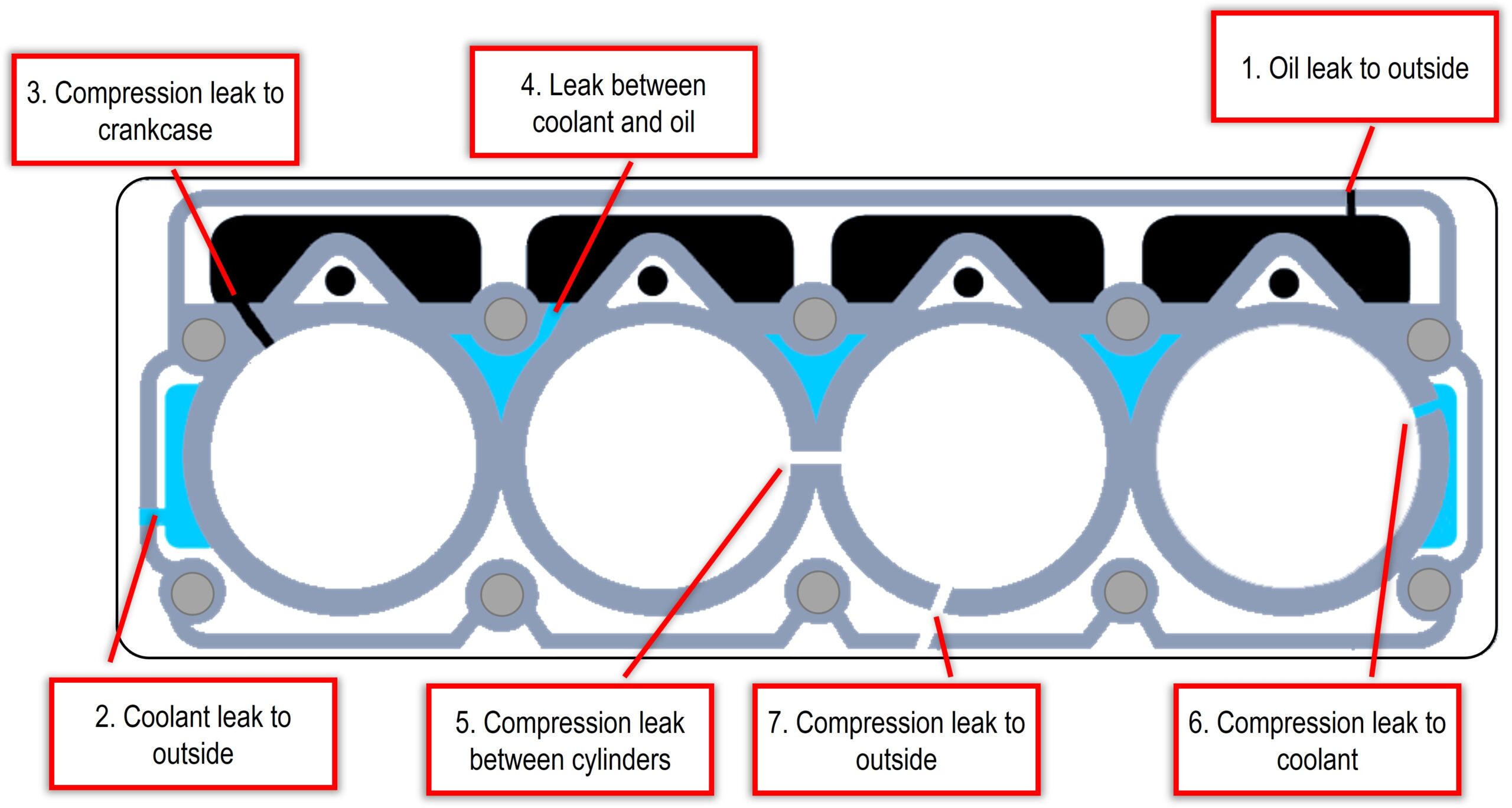
| Head Gasket | Seals the engine block and cylinders, critical in preventing leaks. |
Each component must function correctly to prevent leaks and ensure the engine remains at optimal temperature. If even one part fails, it can potentially lead to coolant escaping the system.
Symptoms And Consequences Of Low Oil Levels
Knowing the symptoms and consequences of low oil levels is essential for all car owners. Oil is the lifeblood of your vehicle’s engine. It keeps it cool and lubricated. Without enough oil, things can go south quickly. Let’s dive into what to watch for and the potential risks of driving with low oil levels.
Warning Signs Of Insufficient Oil
It’s vital to catch the warning signs early to prevent costly repairs. Here are the symptoms to look out for:
- Oil Pressure Warning Light: When the oil level is too low, the oil pressure drops, triggering this light on your dashboard.
- Engine Noise: Low oil can cause your engine to make loud, unusual noises due to increased friction.
- Overheated Engine: Oil helps to dissipate heat. Less oil means more heat, and that could mean an overheating engine.
Potential Damage From Oil Starvation
The engine could suffer a variety of issues without enough oil. Here are some consequences:
| Component | Potential Damage |
|---|---|
| Bearings | Increased wear leading to failure |
| Cylinders and Pistons | Scoring and seizing from friction |
| Overall Engine | Complete engine failure, an expensive outcome |
Remember, frequent checks and maintaining oil levels help keep your vehicle running smoothly and prevents these severe complications.
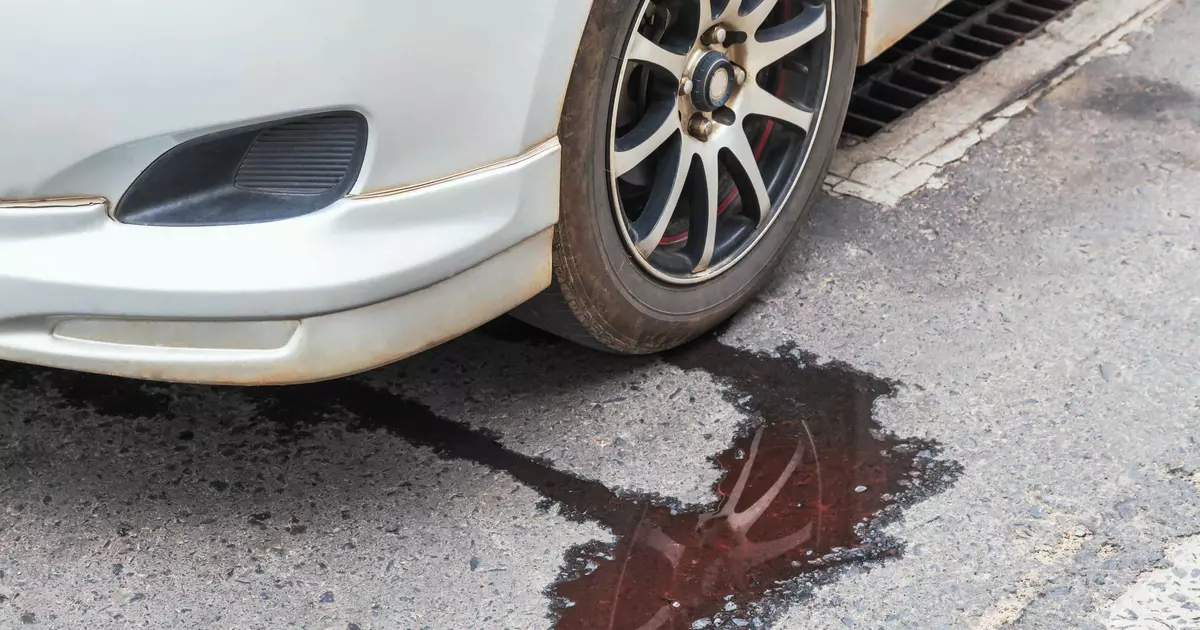

Credit: haynes.com
Exploring The Link Between Oil And Coolant
Understanding your car’s inner workings is key to maintaining its health. Oil and coolant are the lifelines that keep your engine running smoothly. But could there be a hidden link between them, especially when low oil levels come into play? Let’s dive into this engine conundrum and separate fact from fiction when it comes to oil levels and coolant leaks.
Can Low Oil Directly Cause A Coolant Leak?
At first glance, it may seem that oil and coolant systems are independent. Low oil itself doesn’t punch holes in coolant reservoirs or radiators. Yet, ignoring low oil levels can start a chain reaction. This reaction does not cause leaks directly, but it can lead to engine problems that increase the risk of a leak.
Indirect Effects Of Low Oil On Coolant Systems
- Overheating: Oil lubricates parts, reducing friction. Without enough oil, parts overheat, affecting the coolant system.
- Increased Pressure: Overheating parts can cause increased pressure, straining hoses and gaskets, leading to leaks.
- Wear and Tear: Oil keeps engine parts running smoothly. Long-term low oil can lead to premature wear, potentially impacting the coolant system.
To avoid these indirect risks, regularly check your oil levels and address any leaks promptly. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, especially with complex engine systems.
Diagnosing And Resolving Coolant Leaks
A vehicle’s cooling system keeps the engine at the proper temperature. A coolant leak can lead to overheating and engine damage. Understanding how to diagnose and resolve these leaks is crucial for car health. Here’s how to identify and fix common coolant leak issues.
Common Causes Of Coolant Leaks
- Corroded Radiator: Over time, the radiator can rust, leading to leaks.
- Worn Hoses: Hoses deteriorate and may develop cracks or holes.
- Faulty Gaskets: Engine heat can damage gaskets, causing leaks.
- Water Pump Issues: A failing water pump can leak coolant.
- High Pressure: Excessive pressure can cause components to fail and leak.
Steps To Diagnose A Coolant Leak
- Visual Inspection: Check for visible signs of leakage on the ground.
- Check Radiator Hoses: Look for any cracks or splits on the hoses.
- Inspect the Radiator: Search for corrosion or damage.
- Pressure Test: Perform a pressure test to find hidden leaks.
- Consult a Mechanic: If unable to locate the leak, seek professional help.
Credit: f87.bimmerpost.com
Maintaining Your Vehicle To Prevent Leaks
Maintaining your vehicle is crucial to preventing leaks, including those between oil and coolant systems. Regular checks and balances ensure a healthy engine. Ignoring maintenance can lead to issues such as low oil levels, which may indirectly cause coolant leaks. Let’s explore how to keep your car running smoothly.
Regular Maintenance Schedule For Oil And Coolant
Following a maintenance schedule for your vehicle is essential. Here’s a basic guide to help:
- Check oil levels every month.
- Change oil every 5,000 to 7,500 miles or as per manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Inspect coolant levels at each oil change.
- Flush and replace coolant every 30,000 miles or every 2 to 3 years.
Adhering to these intervals is key. Promptly address any discrepancies to avoid complications.
Best Practices For Engine Care
Good engine care practices extend the life of your vehicle. Follow these simple tips:
| Engine Component | Care Practice |
|---|---|
| Air Filter | Replace every 12,000 to 15,000 miles. |
| Spark Plugs | Check every 30,000 miles, replace if needed. |
| Battery | Clean terminals, check charge regularly. |
| Hoses & Belts | Inspect for wear, replace as necessary. |
Monitor for unusual noises or smells from the engine. Seek professional help immediately if something seems off. Routine engine care prevents major repairs and keeps your car running smoothly.

Credit: autorepairseattle.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Can Low Oil Cause Coolant Leak
Can Low Oil Levels Cause A Coolant Leak?
No, low oil levels cannot directly cause a coolant leak. However, inadequate lubrication from low oil might lead to engine overheating, which can stress engine components and potentially lead to coolant system failure and leaks.
How Do Oil And Coolant Systems Interact?
Oil and coolant systems in a vehicle function independently but are both vital for engine temperature regulation. Oil lubricates moving parts, while coolant absorbs heat from the engine to prevent overheating. A malfunction in one system can indirectly affect the other.
What Are Common Signs Of A Coolant Leak?
Common signs of a coolant leak include visible coolant puddles under the vehicle, a sweet antifreeze smell, engine overheating, and low coolant levels. Consistent need to refill coolant can also indicate a leak in the system.
What Should You Do If You Suspect A Coolant Leak?
If you suspect a coolant leak, check the coolant level in the reservoir. Look for signs of a leak such as puddles or residue. If a leak is found or suspected, consult a mechanic immediately to avoid engine damage due to overheating.
Conclusion
Understanding your vehicle’s needs is crucial. Low oil doesn’t directly cause a coolant leak, but neglect can lead to severe issues. Regular maintenance checks are imperative. Remember, a well-oiled engine is less prone to overheating, thus safeguarding coolant integrity. Stay vigilant with routine inspections to prevent costly damage.